- Vitamin D and COVID-19: Is There a Need to Re-evaluate Supplementation Standards?
- Vitamin D Life - Is 50 ng of vitamin D too high, just right, or not enough for all health problems
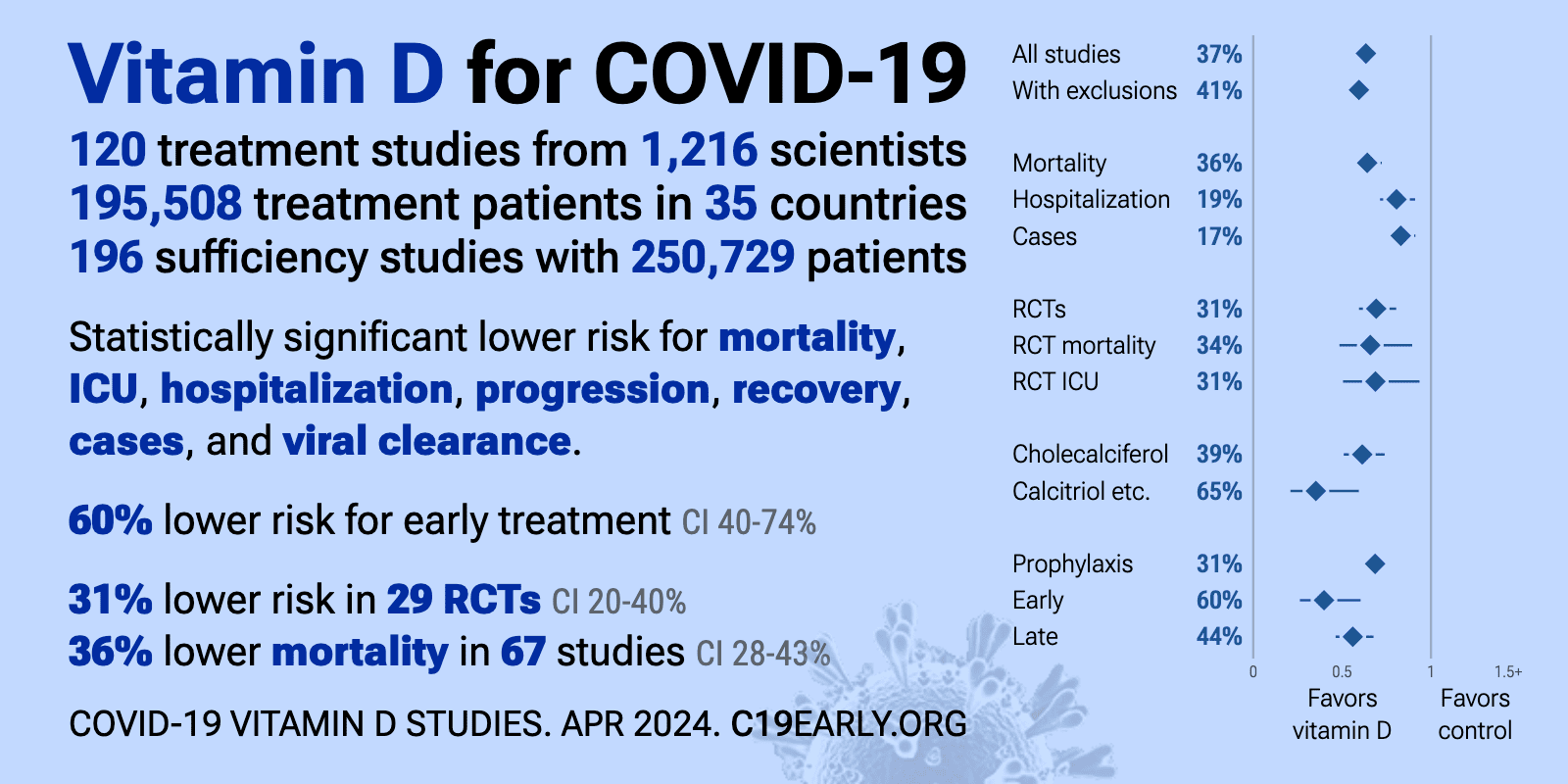
- Vitamin D Life – COVID-19 treated by Vitamin D - studies, reports, videos
- 10+ Vitamin D Life Virus pages have 50 ng in the title
- 75+ pages have 50 ng in Vitamin D Life title
Vitamin D and COVID-19: Is There a Need to Re-evaluate Supplementation Standards?
The COVID-19 pandemic exposed the need for proper strengthening of the immune system. One recent focus to do this has been maintaining a normal vitamin D level. Scientists like Dr. Paul Marik suggest that the average person should have vitamin D levels higher than 50 ng/mL. However, researchers question how much is truly enough. This discussion is coming due to the growing evidence that vitamin D may help improve the severity of COVID-19 cases. However, the National Institutes of Health (NIH) does not endorse this idea. TrialSite followed a study suggesting that vitamin D supplementation shortened hospital stays for COVID-19 patients and decreased mortality rates. This article dives into the NIH's stance on vitamin D for COVID-19 and discusses other published work on this matter.
Vitamin D has gained significant attention in recent years, with much research showing its potential health benefits in diseases like cancer and inflammatory diseases. Since the pandemic, some research on vitamin D has also claimed it can help treat or prevent COVID-19 infections. However, the role of vitamin D in COVID-19 is still being debated among experts.
Vitamin D and COVID-19
With the COVID-19 pandemic came a global crisis that many scientists sought to resolve quickly. They recommended a few supplements including vitamin D to prevent and manage COVID-19. A Cureus article stated that researchers had found a high prevalence of deficient vitamin D levels in COVID-19 patients who were critically ill.
The article also referenced a 2023 Current Nutrition Reports review, showing that maintaining adequate vitamin D3 levels through supplementation could help overcome COVID-19 infection, with improved prognosis and higher survival rates, in frail elders. For this study, the first group had received vitamin D supplements for a year before contracting COVID-19 and being hospitalized. The second group had received a single oral dose of 80,000 IU vitamin D3 after being diagnosed with COVID-19 and the third group, the control group, received no vitamin D supplements. The survival rates were: Group 1 (93.1%), Group 2 (81.2%) and Group 3 (68.7%), respectively.
From the results, the first group had a longer survival time, in other words, a longer length of time a participant remained alive after being diagnosed with COVID-19 than the second. There was no statistically significant difference between the second and third groups. Even so, a pattern in the results illustrated that taking vitamin D supplements even after contracting COVID-19 is still better than not taking it at all.
However, using vitamin D for COVID-19 remains controversial as some scientists disagree with its use. For example, a 2022 study published in JAMA Network clearly stated, “Vitamin D supplements don’t reduce COVID-19 risk.” The study involved a large UK trial involving 6200 participants over the age of 16.
The researchers conducted a vitamin D blood test on half of the participants, and among those tested, 86% had suboptimal vitamin D levels. The individuals with suboptimal levels were then given either 800 IU/d or 3200 IU/d of vitamin D supplements for six months. The remaining half of the participants did not undergo testing or receive any supplements. Neither of the two vitamin D doses showed a significant impact on the occurrence of all-cause acute respiratory tract infections or specifically on COVID-19 cases when compared to the control group.
Another similar 2022 study suggested no clear correlation between vitamin D status and the clinical severity or pulmonary involvement of COVID-19 in pregnant women. The study compared pregnant women infected with SARS-CoV-2 to healthy pregnant women and found that both groups had similar rates of vitamin D deficiency or adequacy.
The NIH’s recommendation
The NIH doesn’t support vitamin D supplementation for preventing or managing COVID-19 cases. According to the organization, “There is insufficient evidence for the COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines Panel (the Panel) to recommend either for or against the use of vitamin D for the prevention or treatment of COVID-19.”
The NIH added that most studies supporting the use of vitamin D for COVID-19 prevention had limitations such as small sample sizes and varying doses and formulations of vitamin D. As such, they were not solid proof to recommend the supplement for COVID-19 prevention or management. However, based on available evidence, they agree that people with deficient vitamin D levels may have an increased risk of getting a COVID-19 infection and have worse clinical outcomes post-infection.
What then does the NIH recommend? The NIH states, “Data are insufficient to support recommendations for or against the use of any vitamin, mineral, herb or other botanical, fatty acid, or other dietary supplement ingredient to prevent or treat COVID-19.” They added that legal regulations prohibit promoting dietary supplements as treatments, preventions, or cures for any disease. Only drugs have the legal authority to make such claims.
Is the more the merrier?
Aside from recommending vitamin D for COVID-19, scientists like Marik also suggest targeting 55-90 ng/mL for optimal health, emphasizing levels above 50 ng/mL specifically for COVID-19. However, the NIH considers this too high.
Marik is a Professor of Medicine and Chief of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine at Eastern Virginia Medical School (EVMS), Virginia. He also co-founded the Frontline COVID-19 Critical Care Alliance (FLCCC) and was previously charged with prescribing ivermectin for COVID-19 treatment. Marik has frequently advised targeting higher 50 ng/mL vitamin D benchmarks as in the FLCCC prevention and treatment protocols for COVID-19 that he co-developed. His latest cancer care guide also endorses maintaining such levels through ongoing supplementation.
Another scientist supporting more vitamin D for COVID-19 is Dr. William B. Grant, director of Sunlight, Nutrition and Health Research Center (SUNARC). In an interview with the FLCCC, Grant mentioned that people with influenza or COVID-19 should consider taking 10,000 IU per day to raise their vitamin D3 levels. They should then subsequently reduce the dosage to 5000 IU per day. Grant stated that the goal was to raise vitamin D3 levels above 40-60 ng/mL and suggested even higher doses for people infected with COVID-19.
Grant also added that for most diseases, the greatest benefits of vitamin D occur at levels below 20 ng/mL. However, in the case of a COVID-19 infection, the concept of a triage theory is introduced. This means that as vitamin D levels increase, the body prioritizes delivering it to areas where it's most urgently needed for immediate survival. For example, during a COVID-19 infection, the body might allocate vitamin D to address the immediate threat rather than focusing on longer-term concerns like cancer.
During the interview, Grant also shares a personal experience of taking over 100 ng/mL of vitamin D during a bout of COVID-19 at the age of 81. Despite being in a high-risk age group, he experienced only five days of COVID-19 symptoms, including a sore throat, with no significant adverse effects. He also added he did not have any comorbid disease that may have increased the risk of severe illness. The implication is that maintaining higher vitamin D levels may have contributed to a less severe course of the illness.
An Oxford study supporting this claim
Here we consider a 2022 Oxford Academic study involving forty individuals with positive SARS-CoV-2 RNA, randomly assigned to either an intervention or control group. The intervention group was administered 60,000 IU of vitamin D daily for seven days. The researchers were targeting vitamin levels >50 ng/ml for this group. While participants received the supplement, tests for SARS-CoV-2 and several inflammation markers like fibrinogen and ferritin were repeated regularly.
The researchers noticed that by day seven, ten out of 16 participants in the intervention group had achieved vitamin D levels greater than 50 ng/mL, and two more had reached this level by day 14. Ten participants in the intervention group and five participants in the control became SARS-CoV-2 RNA negative. The study suggests that more vitamin D-deficient individuals with SARS-CoV-2 infection became SARS-CoV-2 RNA negative after receiving high doses of vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) for seven days. NHANES data evaluated the population's vitamin D intake.
The researchers also noticed a substantial decline in fibrinogen levels with vitamin D supplementation. Elevated fibrinogen levels have been associated with COVID-19 severity. The decline in fibrinogen levels aligns with the negative results obtained for SARS-CoV-2 by the researchers.
Given that studies endorsed by the NIH suggest a correlation between deficient vitamin D levels and an elevated risk of COVID-19, it raises the question of how many individuals are genuinely consuming sufficient vitamin D supplements to be considered adequate according to NIH standards.
The NHANES program
The NHANES is a program comprising a series of studies evaluating the health and nutritional well-being of both adults and children in the United States. The NHANES data from the years 2017-2018 evaluated serum vitamin D levels in the US population. It made this analysis by taking note of different forms of vitamin D in the body: 25-hydroxyvitamin D2 + D3 (VIDMS), 25-hydroxyvitamin D2 (VD2MS), 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 (VD3MS) and epi-25-hydroxyvitamin D3 (VE3MS).
| Range (ng/ml) | Percentage |
| 0-10 | 4.05 |
| 10-20 | 24.19 |
| 20-30 | 38.94 |
| 30-40 | 21.61 |
| 40-50 | 7.38 |
| 50-60 | 2.57 |
| 60-70 | 0.80 |
| 70-80 | 0.23 |
| 80-90 | 0.18 |
| 90-100 | 0.01 |
| 100-110 | 0.03 |
| 110-140 | 0.00 |
| 140-150 | 0.01 |
| 150-160 | 0.00 |
| 160-170 | 0.01 |
| Over 170 | 0.00 |
From the survey involving 7401 individuals, only 67.9% of participants fulfill the NIH criteria of 20-50 ng/mL (includes sets 20-30, 30-40 and 40-50 ng/mL), while 28.2% of these participants are not fulfilling the NIH’s criteria. However, if the level should be 50 ng/mL and above then only 3.84% of people have the correct levels. So, by either standard, a concerning percentage of the population consumes suboptimal amounts of vitamin D and is unable to support health.
What do other major medical organizations say?
The UK National Health Service (NHS) states that a serum vitamin D level ≥30 ng/mL (75 nmol/L) is considered adequate. They say that there might be added advantages associated with levels ranging between 36-40 ng/mL (90-100 nmol/L). If the NHS guidelines are correct, then only 21.61% of people are achieving adequate vitamin D levels while 67.18% are not, per the NHANES data. The NHS also aligns with the NIH by frowning on the use of vitamin D for COVID-19 prevention.
UK scientists also advise against taking high levels of vitamin D to prevent or treat COVID-19. The NHS advises that it’s crucial to exercise caution as excessive vitamin D levels can be harmful. Public Health England (PHE) recommends a low-dose vitamin D supplement for general health, acknowledging that while it may have general benefits, any potential extra advantage for COVID-19 would be an added benefit.
Leading medical organizations like the Endocrine Society, the International Osteoporosis Foundation (IOF), and the American Geriatric Society (AGS) agree that vitamin D deficiency occurs when blood levels of 25-hydroxyvitamin D fall below 30 ng/mL. The Endocrine Society suggests levels between 40 and 60 ng/mL for optimal bone health benefits. Per the NHANES data, only 9.95% of the population is attaining optimal vitamin D levels and 88.79% are not, going by the Endocrine Society’s suggestion. To achieve this optimal range, the recommended daily intake of vitamin D varies by age: 400-1000 IU for infants under the age of one, 600-1000 IU for children and adolescents, and 1500-2000 IU for adults.
A need to re-evaluate the standards
TrialSite previously reported on researchers’ opinions and findings on optimal vitamin D levels to maintain good health, and in this piece, we dig deeper into the claim that vitamin D levels are important for COVID-19 prevention and management.
Marik’s findings and supporting studies we mentioned contribute to evidence suggesting that prevailing vitamin D guidelines established before the pandemic may insufficiently optimize the immune system against COVID-19 specifically. This begs the question of whether there’s a need to re-examine the vitamin D guidelines.
However, it’s important to note the side effects of vitamin D toxicity, such as elevated blood levels and kidney complications. Nonetheless, as data keeps linking adequate vitamin D status with lower COVID-19 susceptibility, there might be a case for re-evaluating standards in the context of the COVID-19 infection.
Vitamin D Life - Is 50 ng of vitamin D too high, just right, or not enough for all health problems
Vitamin D Life – COVID-19 treated by Vitamin D - studies, reports, videos
As of March 31, 2024, the Vitamin D Life COVID page had: trial results, meta-analyses and reviews, Mortality studies see related: Governments, HealthProblems, Hospitals, Dark Skins, All 26 COVID risk factors are associated with low Vit D, Fight COVID-19 with 50K Vit D weekly Vaccines Take lots of Vitamin D at first signs of COVID 166 COVID Clinical Trials using Vitamin D (Aug 2023) Prevent a COVID death: 9 dollars of Vitamin D or 900,000 dollars of vaccine - Aug 2023
5 most-recently changed Virus entries
- The above image is automatically updated
10+ Vitamin D Life Virus pages have 50 ng in the title
This list is automatically updated
75+ pages have 50 ng in Vitamin D Life title
This list is automatically updated