Genetic Polymorphisms in the Vitamin D Pathway and Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Survival
Pathology & Oncology Research, pp 1–7
Jinyu Kong Xiaojie Chen Jian Wang Jingxin Li Fangxiu Xu Shegan Gao Herbert Yu Biyun Qian
49 items in Cancer-Lung - see also Overview Lung cancer and vitamin D, Cancer - After diagnosis, Overview Cancer and vitamin D
Lung Cancer Meta-analyses
- Lung Cancer more likely if poor Vitamin D Receptor – meta-analysis June 2019
- Lung Cancer risk decreased 2.4 percent with every 100 IU Vitamin D extra intake – meta-analysis Sept 2018
- Lung Cancer patients were 2.4 times more likely to have a poor Vitamin D Receptor gene – July 2017
- Lung Cancer death 60 percent less likely if high level of vitamin D – 2 meta-analysis 2017
- Lung Cancer risk decreases 5 percent for every 2.5 nanogram increase in Vitamin D – meta-analysis Sept 2015
- Lung Cancer less likely if vitamin D (higher level or supplement) – meta-analysis May 2015
Lung Cancer Genetics
Lung Cancer Vitamin D Receptor
Wikipedia

From the web

Download the PDF from Vitamin D Life
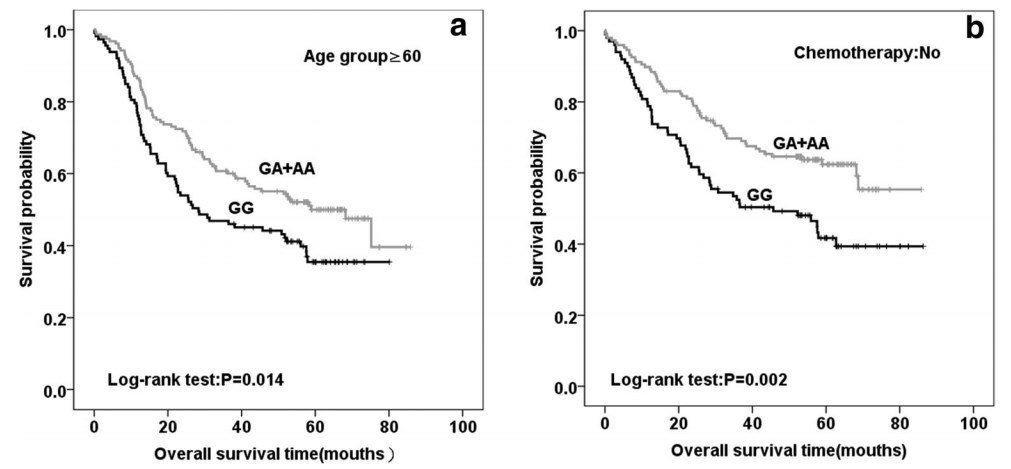
Note: Trends for two additional genes
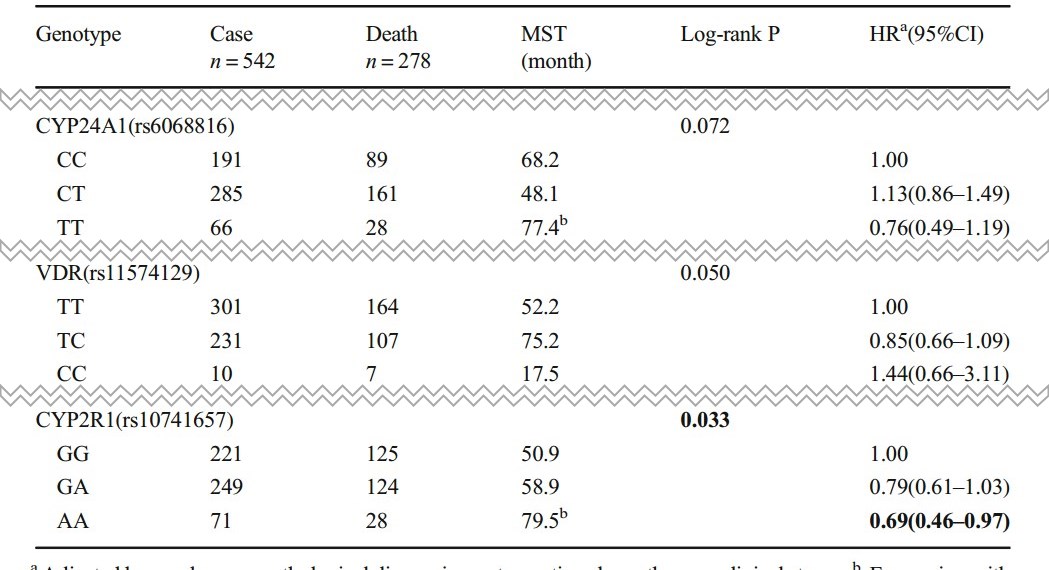
Various genetic polymorphisms have been linked to lung cancer susceptibility and survival outcomes. Vitamin D (VD) regulates cell proliferation and differentiation, inhibits tumor growth and induces apoptosis. Observations from several previous studies including our own suggest that genetic polymorphisms in the VD pathway may be associated with lung cancer risk. The aim of this study is to assess if genetic polymorphisms in the VD pathway are associated with the prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Nine single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in five genes in the VD pathway were genotyped with the TaqMan assays in 542 patients with primary NSCLC, and the relationships between these SNPs and overall survival were evaluated.
We found that SNP rs10741657 in the CYP2R1 gene was associated with the prognosis of NSCLC, especially in elderly patients and not being treated with chemotherapy. Some of the VD pathway-related genetic polymorphisms may influence the prognosis of NSCLC. More research is needed to further confirm the finding and test if VD supplements can be used for NSCLC treatment.
Lung Cancer (NSLC) more lethal if poor Vitamin D gene ( CYP2R1) – Oct 2019 702 visitors, last modified 17 Oct, 2019,
Printer Friendly PDF this page! Follow this page for updates This page is in the following categories (# of items in each category) Genetics 266 Cancer - Lung 49 Attached files
ID Name Comment Uploaded Size Downloads 12817 Lung Cancer types.jpg admin 17 Oct, 2019 20:52 24.19 Kb 147 12816 NSLC Wikipedia.jpg admin 17 Oct, 2019 20:50 95.35 Kb 147 12815 NSLC table.jpg admin 17 Oct, 2019 20:32 105.91 Kb 158 12814 NSLC.jpg admin 17 Oct, 2019 20:31 53.81 Kb 154 12813 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer.pdf PDF 2019 admin 17 Oct, 2019 20:30 272.77 Kb 157
See any problem with this page? Report it (FINALLY WORKS)
- see also Overview Lung cancer and vitamin D, Cancer - After diagnosis, Overview Cancer and vitamin D
Lung Cancer Meta-analyses
- Lung Cancer more likely if poor Vitamin D Receptor – meta-analysis June 2019
- Lung Cancer risk decreased 2.4 percent with every 100 IU Vitamin D extra intake – meta-analysis Sept 2018
- Lung Cancer patients were 2.4 times more likely to have a poor Vitamin D Receptor gene – July 2017
- Lung Cancer death 60 percent less likely if high level of vitamin D – 2 meta-analysis 2017
- Lung Cancer risk decreases 5 percent for every 2.5 nanogram increase in Vitamin D – meta-analysis Sept 2015
- Lung Cancer less likely if vitamin D (higher level or supplement) – meta-analysis May 2015
Lung Cancer Genetics
Lung Cancer Vitamin D Receptor
Wikipedia
From the web
Download the PDF from Vitamin D Life
Note: Trends for two additional genes
Various genetic polymorphisms have been linked to lung cancer susceptibility and survival outcomes. Vitamin D (VD) regulates cell proliferation and differentiation, inhibits tumor growth and induces apoptosis. Observations from several previous studies including our own suggest that genetic polymorphisms in the VD pathway may be associated with lung cancer risk. The aim of this study is to assess if genetic polymorphisms in the VD pathway are associated with the prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Nine single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in five genes in the VD pathway were genotyped with the TaqMan assays in 542 patients with primary NSCLC, and the relationships between these SNPs and overall survival were evaluated.
We found that SNP rs10741657 in the CYP2R1 gene was associated with the prognosis of NSCLC, especially in elderly patients and not being treated with chemotherapy. Some of the VD pathway-related genetic polymorphisms may influence the prognosis of NSCLC. More research is needed to further confirm the finding and test if VD supplements can be used for NSCLC treatment.
| 702 visitors, last modified 17 Oct, 2019, |
| ID | Name | Comment | Uploaded | Size | Downloads | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12817 | Lung Cancer types.jpg | admin 17 Oct, 2019 20:52 | 24.19 Kb | 147 | ||
| 12816 | NSLC Wikipedia.jpg | admin 17 Oct, 2019 20:50 | 95.35 Kb | 147 | ||
| 12815 | NSLC table.jpg | admin 17 Oct, 2019 20:32 | 105.91 Kb | 158 | ||
| 12814 | NSLC.jpg | admin 17 Oct, 2019 20:31 | 53.81 Kb | 154 | ||
| 12813 | Non-small Cell Lung Cancer.pdf | PDF 2019 | admin 17 Oct, 2019 20:30 | 272.77 Kb | 157 |
